Create Modal
New Modal Creation
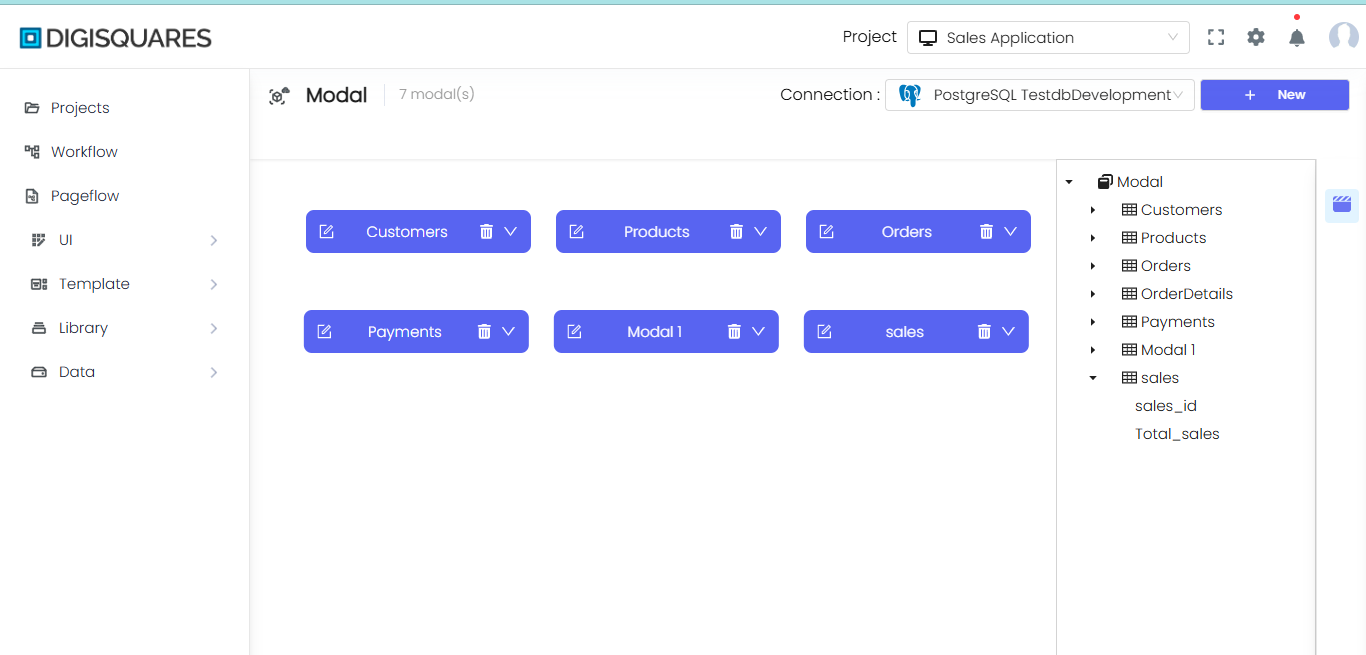
The New Modal interface enables you to define the structure and schema for your database table. A modal serves as the blueprint for the table's properties, ensuring that the fields are properly defined, along with their corresponding data types and constraints. This guide walks you through the key features of the New Modal interface.
Example Chart Visualizations
Here are some example visualizations created using Digisquares:
Interface Overview
-
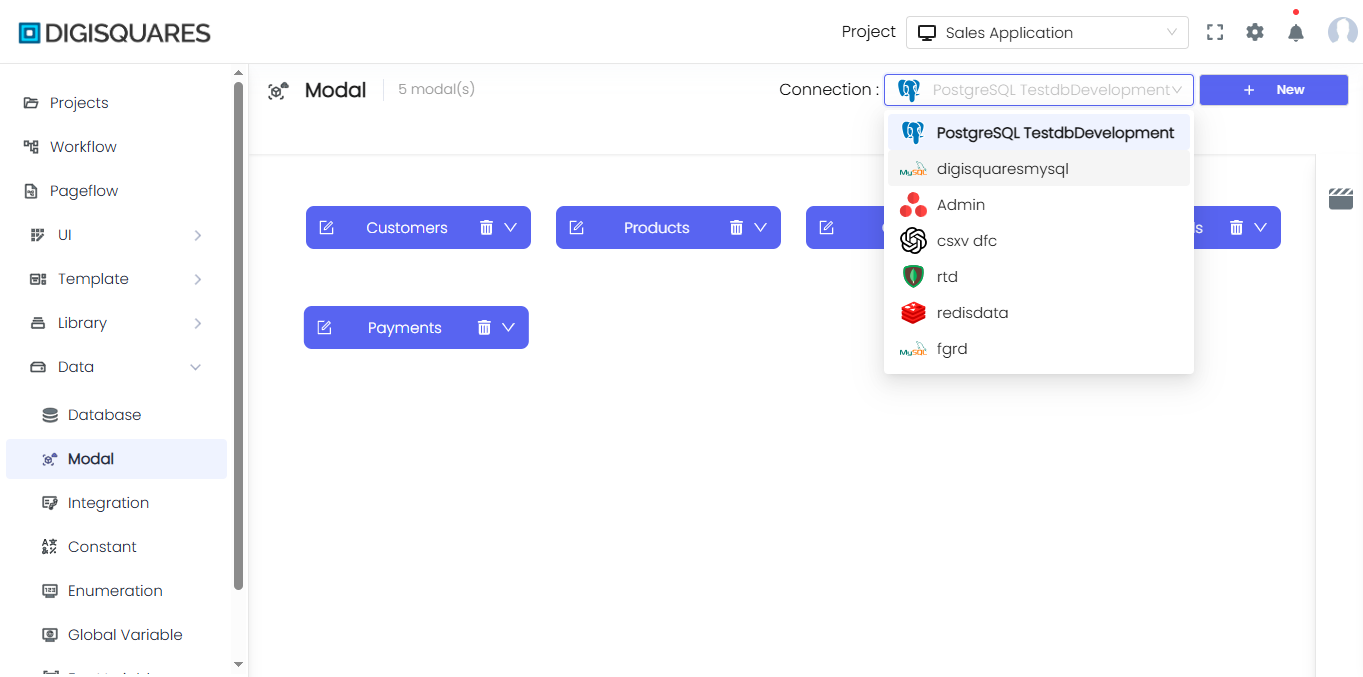
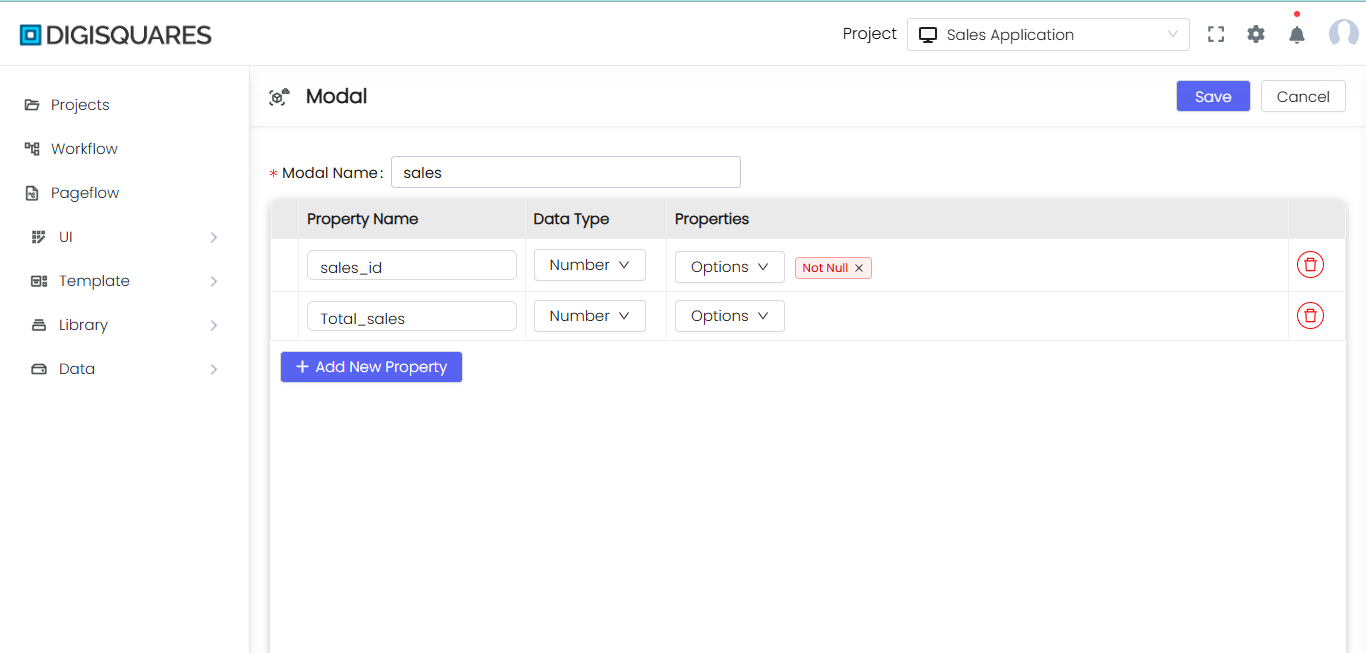
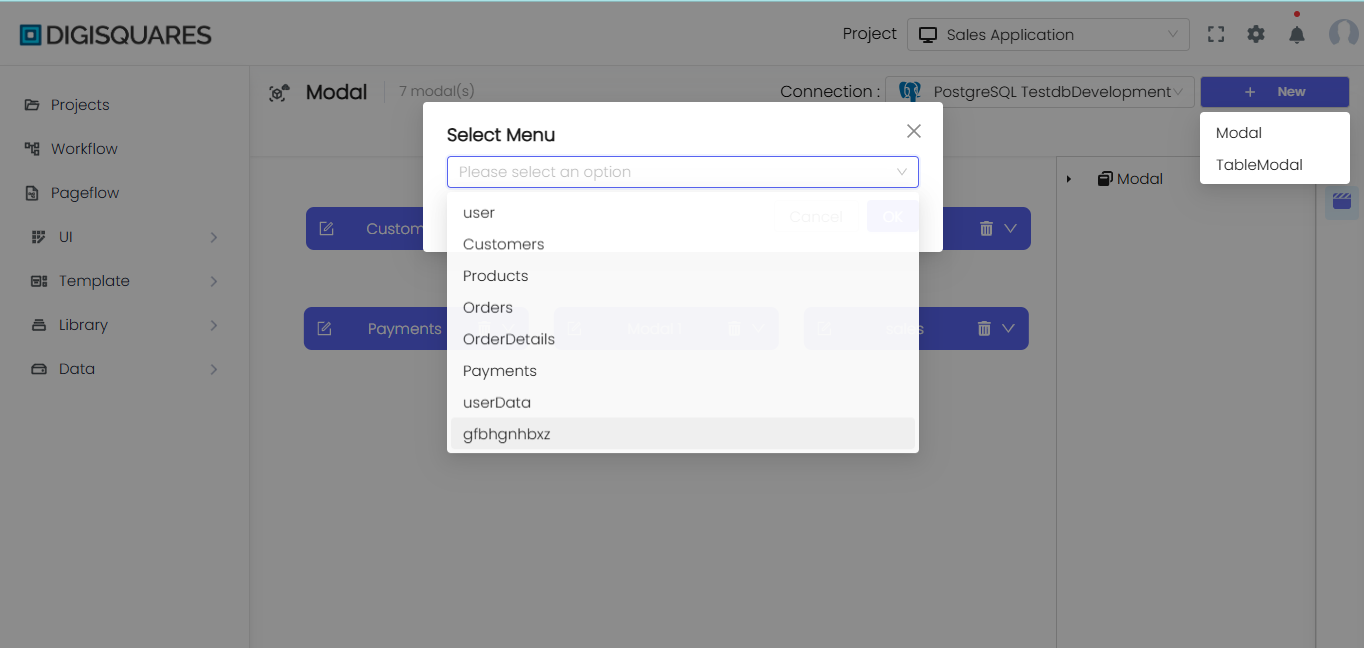
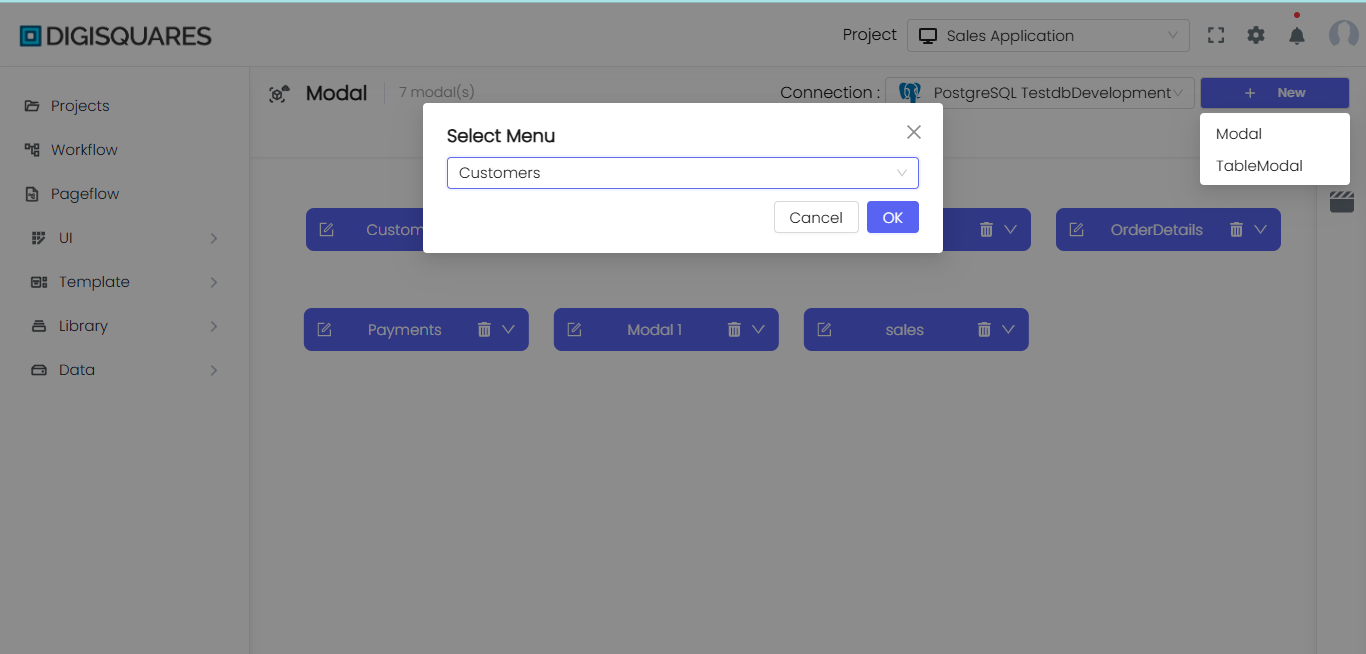
Modal Name:
- This field allows you to specify a name for the modal, representing the overall schema or entity you're defining.
- Example:
Modal 1in the image represents a basic modal with fields such asProperty 1,name, andage.
-
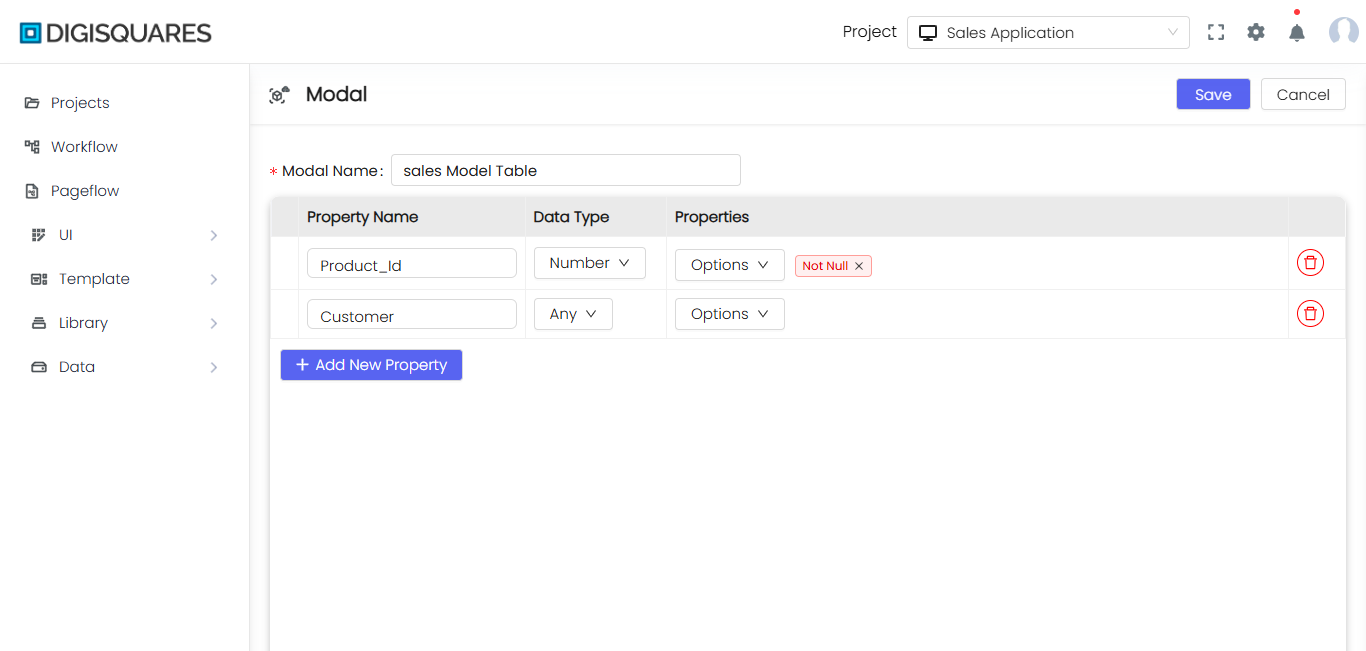
Property Name:
- Property names represent the fields (columns) of your modal. Each property will have its own unique name.
- Example:
Property 1,name, andageare the properties in the modal.
-
Data Type:
- Defines the type of data the field will hold. This ensures that each property contains data in the correct format.
- Available data types include:
- String: For textual data such as names, descriptions, or addresses.
- Number: For numeric data such as ages, quantities, or IDs.
- Boolean: For true/false values, commonly used for status flags (e.g.,
is_active). - Any: Accepts any type of data, offering flexibility when the data type is not fixed or can vary.
- Array: Stores a list of values, useful for fields that hold multiple related items (e.g., multiple skills).
- Object: Stores key-value pairs, useful for more complex structured data (e.g., an employee's salary breakdown).
- BigInt: Used for large integers, often required for precise numerical operations that exceed the limits of standard
Numbertypes.
- Example: In the image, the data types are
Boolean,String, andNumberfor the respective properties.
-
Properties:
- This section allows you to configure constraints and validation rules for each field. You can add various properties such as
Not Null,Optional,Relation Key,Max Value, andMin Value.
Property Options Explained:
- Not Null: Ensures the field cannot have null or empty values.
- Optional: Allows the field to be null or empty.
- Relation Key: Defines the field as a foreign key, linking it to another table.
- Max Value: Specifies the maximum allowed value for a numeric field.
- Min Value: Specifies the minimum allowed value for a numeric field.
- Example:
- The field
namehas aRelation Key, indicating it’s linked to another table. - The field
agehasMax Valueof 10,Min Valueof 1, and is marked asOptionalbut alsoNot Null, ensuring flexible validation.
- The field
- This section allows you to configure constraints and validation rules for each field. You can add various properties such as
-
Add New Property:
- Click this button to add a new field (property) to the modal. This allows you to extend the schema by defining additional fields and their properties.
-
Actions Available:
- Save: Saves the modal and applies the defined schema to the table in the database.
- Cancel: Discards the changes made to the modal and returns to the previous screen without saving.
Example Modal Configuration:
Modal Name: Employee
| Property Name | Data Type | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| employee_id | Number | Not Null, Auto Increment, Primary Key |
| employee_name | String | Not Null |
| skills | Array | Optional |
| department_id | Number | Relation Key (links to departments table) |
| hire_date | Date | Not Null, Optional |
| salary_details | Object | Optional, Stores structured key-value data |
| is_active | Boolean | Default True |
| large_salary | BigInt | Not Null |
Explanation:
- The employee_id field is a unique identifier with
Auto IncrementandPrimary Keyproperties. - The department_id field is a foreign key (Relation Key) that links to the
departmentstable. - The skills field is an Array, allowing you to store multiple skills related to the employee.
- The salary_details field is an Object, storing complex data like salary breakdown (e.g., base salary, bonuses).
- The large_salary field is a BigInt, ensuring accurate storage of very large salary amounts.
Benefits of Using Different Data Types:
- String: Ideal for storing textual information like names, addresses, and descriptions.
- Number: Perfect for numeric values, IDs, and quantities.
- Boolean: Simplifies managing flags such as
is_active, which can either betrueorfalse. - Any: Provides flexibility when data types are uncertain or dynamic.
- Array: Useful for storing multiple related values (e.g., multiple skills, tags, or categories).
- Object: Enables you to store complex data in key-value pairs (e.g., employee’s salary breakdown).
- BigInt: Ensures accurate calculations and storage for very large numbers, particularly when dealing with financial figures.
Summary
The New Modal interface allows you to easily create and manage database schemas by defining fields, data types, and properties. It supports simple and complex structures like arrays and objects, while ensuring flexibility, data integrity, and control over relationships and constraints. This intuitive tool streamlines database management, helping you design and extend tables efficiently.